Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Surgery: Understanding the Basics
Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary surgery is a specialized branch of surgery that deals with diseases of the digestive system and liver. The digestive system is a complex network of organs that includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The liver, on the other hand, is the largest organ in the body, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
The digestive system plays a critical role in the body by breaking down food into nutrients that the body can use for energy, growth, and repair. Any disruption in this process can lead to various gastrointestinal diseases that require surgical intervention. Similarly, the liver performs essential functions such as filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile, and storing glucose. When the liver is damaged or diseased, hepatobiliary surgery becomes necessary.
Some of the most common gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary surgeries include:
- Appendectomy: This is the surgical removal of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. Appendectomy is usually done to treat appendicitis, a condition where the appendix becomes inflamed and infected.
- Cholecystectomy: This is the surgical removal of the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. Cholecystectomy is usually done to treat gallstones, a condition where solid deposits form in the gallbladder.
- Colectomy: This is the surgical removal of part or all of the large intestine. Colectomy is usually done to treat conditions such as colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or diverticulitis.
- Esophagectomy: This is the surgical removal of the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. Esophagectomy is usually done to treat esophageal cancer or severe reflux disease.
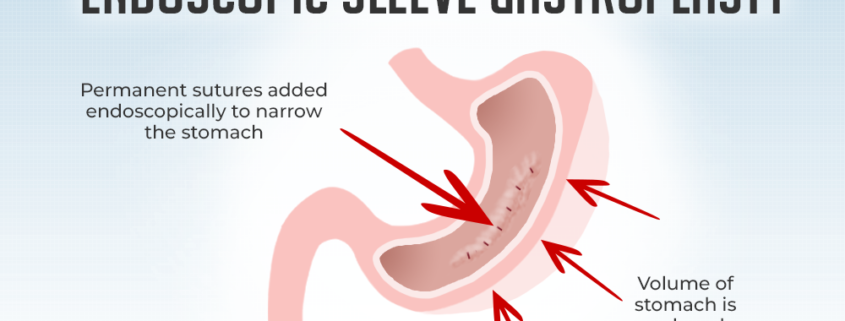
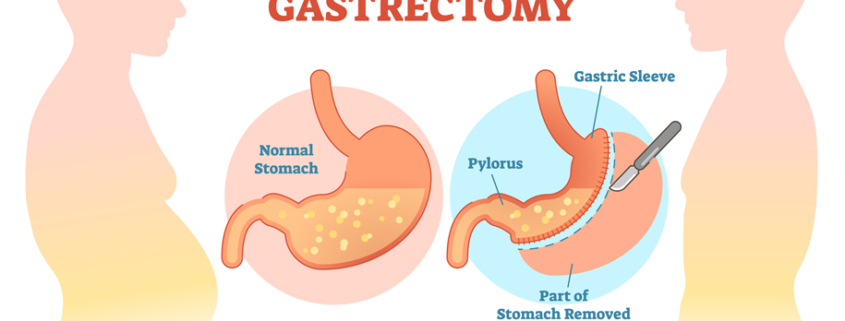
- Gastrectomy: This is the surgical removal of part or all of the stomach. Gastrectomy is usually done to treat stomach cancer or severe ulcers.
- Liver resection: This is the surgical removal of part of the liver. Liver resection is usually done to treat liver cancer, benign liver tumors, or liver disease.
- Pancreatectomy: This is the surgical removal of part or all of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach. Pancreatectomy is usually done to treat pancreatic cancer or severe pancreatitis.
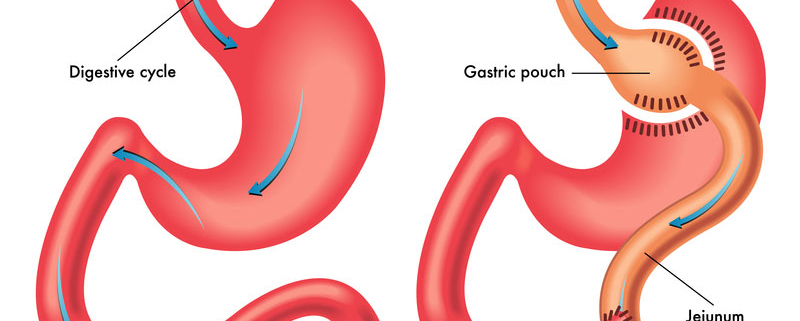
- Whipple procedure: This is a complex surgical procedure that involves the removal of the head of the pancreas, the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine), the gallbladder, and part of the stomach. The remaining organs are then reconnected to allow for normal digestion. The Whipple procedure is usually done to treat pancreatic cancer.
Before any gastrointestinal or hepatobiliary surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to determine the extent of their disease and whether surgery is the best course of action. This evaluation typically includes blood tests, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs, and sometimes endoscopic procedures such as colonoscopy or upper endoscopy.
Once the decision to proceed with surgery is made, the patient is given instructions on how to prepare for the procedure. This may include dietary restrictions, bowel preparation, and cessation of certain medications.
During the surgery itself, the patient is given general anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and do not feel any pain. The surgeon then makes an incision in the abdomen to access the affected organ or organs. The exact approach and technique used will depend on the specific surgery being performed.
After the surgery, the patient is closely monitored in a recovery room to ensure they are stable and not experiencing any complications. They may be given pain medication, antibiotics, and other medications as needed.