Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is a weight loss procedure that is gaining popularity in recent years. ESG is a non-surgical procedure that is performed by a gastroenterologist, and it involves reducing the size of the stomach by creating a sleeve-like shape using an endoscope. In this blog, we will discuss ESG in detail, including how it works, who is a candidate for the procedure, and the potential benefits and risks.
How does Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty work?
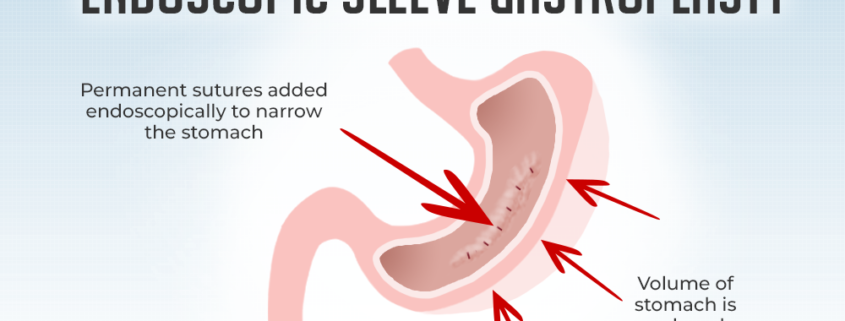
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty works by reducing the size of the stomach. The gastroenterologist uses an endoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a camera and light attached to it, to access the stomach through the mouth. The endoscope is used to create a series of sutures, or stitches, along the inside of the stomach. These sutures are placed in a way that creates a sleeve-like shape, which reduces the volume of the stomach.
The procedure typically takes between one and two hours and is performed under sedation. Patients are usually able to go home on the same day as the procedure.
Who is a candidate for Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty?
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty is typically recommended for people who have a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher and have not been able to achieve weight loss through traditional methods such as diet and exercise. It may also be recommended for people who are not good candidates for traditional weight loss surgeries, such as gastric bypass surgery, due to medical reasons.
However, it is important to note that ESG is not a quick fix for weight loss. Patients must be committed to making long-term lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, in order to achieve and maintain weight loss.
What are the potential benefits of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty?
One of the main benefits of ESG is that it is a non-surgical procedure, which means there is no need for incisions or general anaesthesia. This can lead to a quicker recovery time and fewer complications compared to traditional weight loss surgeries.
Additionally, ESG has been shown to be an effective method for weight loss. Studies have shown that patients can expect to lose an average of 15-20% of their excess body weight within the first year after the procedure.
ESG may also have other health benefits, such as improving blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels.
What are the potential risks of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty?
As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with ESG. These may include bleeding, infection, perforation of the stomach or esophagus, and anaesthesia complications.
In rare cases, the sutures used during the procedure may become loose or come undone, which can lead to a reversal of the weight loss effects.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and complications with your healthcare provider before deciding to undergo ESG.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty is a non-surgical weight loss procedure that involves reducing the size of the stomach using an endoscope. It is typically recommended for people who have not been able to achieve weight loss through traditional methods and who are not good candidates for traditional weight loss surgeries.
ESG has been shown to be an effective method for weight loss, with patients able to expect to lose an average of 15-20% of their excess body weight within the first year after the procedure. Additionally, ESG may have other health benefits, such as improving blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels.
However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with ESG. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before deciding to undergo the procedure