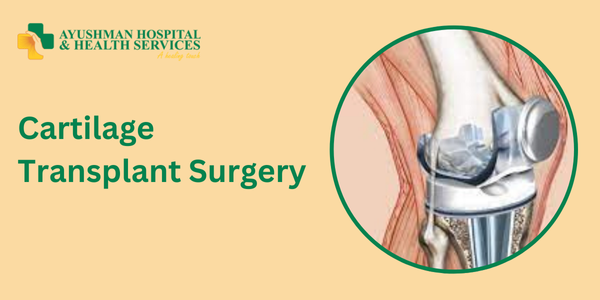
If you or someone you know is dealing with joint pain, limited movement, or a decrease in quality of life, cartilage transplant surgery might be a hopeful option. This innovative procedure aims to relieve pain and restore function in damaged joints. In this blog, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about cartilage transplant surgery at Ayushman Hospital in Dwarka, Delhi. We’ll cover what cartilage is, why it gets damaged, the surgery details, recovery, and why many patients choose Ayushman Hospital for their care. Let’s dive in!
Introduction
Cartilage is a smooth, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of your bones in joints. Think of it as a cushion that helps your joints move smoothly and reduces friction. When cartilage gets damaged—due to injury, aging, or chronic conditions—it can lead to significant pain and limited mobility. Cartilage transplant surgery offers a way to replace damaged cartilage with healthy tissue, helping you regain movement and improve your quality of life.
At Ayushman Hospital in Dwarka, Delhi, patients benefit from advanced medical care and cutting-edge technology. With a team of skilled orthopedic surgeons and dedicated rehabilitation staff, the hospital is committed to helping you heal. This blog is designed to give you a clear understanding of the procedure and why it’s becoming a popular choice for many.
Understanding Cartilage and Its Importance
What is Cartilage?
Cartilage is a flexible yet tough tissue found in various parts of the body, including joints, the rib cage, ears, and nose. In your joints, it covers the ends of bones, allowing them to glide smoothly over one another and acting as a shock absorber. Unlike other tissues, cartilage doesn’t have its own blood supply, which makes it harder for it to heal itself when damaged.
The Role of Cartilage in Joint Function
- Shock Absorption: Cartilage cushions the impact on your joints during activities like walking or running.
- Smooth Movement: Its smooth surface allows bones to move with minimal friction.
- Joint Stability: Healthy cartilage helps stabilize joints by evenly distributing weight.
When cartilage is damaged, it can cause pain, swelling, and reduced movement, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis that make daily activities difficult.
Causes of Cartilage Damage
Understanding what leads to cartilage damage can help you take preventive measures. Here are some common causes:
Traumatic Injuries
Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause sudden damage to cartilage. For example, twisting your knee during a game can lead to a cartilage tear, resulting in immediate pain and swelling.
Degenerative Conditions
Over time, wear and tear on your joints can degrade cartilage. Osteoarthritis is a common condition where cartilage wears away, causing chronic pain and limited mobility.
Genetic Factors
Some people are genetically predisposed to cartilage damage. While you can’t change your genes, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms effectively.
Inflammatory Diseases
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint inflammation, leading to cartilage breakdown over time.
Lifestyle Factors
- Obesity: Extra weight adds stress to your joints, speeding up cartilage wear.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Not exercising regularly can weaken muscles and joints, affecting cartilage health.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients can impair your body’s ability to maintain healthy cartilage.
To prevent further damage, it’s important to adopt a healthy lifestyle, eat well, and seek medical advice if you experience joint pain.
What is Cartilage Transplant Surgery?
Cartilage transplant surgery is a procedure designed to repair or replace damaged cartilage. The goal is to restore joint function, reduce pain, and improve your overall quality of life.
Types of Cartilage Transplant Procedures
Several types of procedures exist, and the right one for you depends on the severity of your cartilage damage:
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI): Healthy cartilage cells are taken from you, grown in a lab, and then re-implanted into the damaged area.
- Osteochondral Autograft Transfer (OAT): A small plug of healthy cartilage and bone is taken from a non-weight-bearing part of your joint and placed in the damaged area.
- Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation: For larger areas of damage, donor tissue is used to replace the defective cartilage.
How Does the Surgery Work?
The process typically involves these steps:
- Assessment and Planning: Imaging studies (like an MRI) are done to assess the damage, and the surgeon plans the best approach.
- Harvesting the Cartilage: Depending on the procedure, your own cartilage or donor cartilage is prepared.
- Implantation: The damaged cartilage is removed, and the healthy cartilage is transplanted into the area.
- Stabilization: Sometimes, devices are used to stabilize the new tissue during healing.
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, and the time it takes can vary based on the complexity of the case.
Who Can Benefit from the Surgery?
Cartilage transplant surgery can be a transformative option, but it’s not for everyone. Here’s who might benefit:
Ideal Candidates
- Young to Middle-Aged Adults: Generally, those who are active and have localized cartilage defects benefit the most.
- Isolated Cartilage Damage: Those with damage confined to one area of the joint, without affecting other structures, are excellent candidates.
- Good Overall Health: Individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle and do not have underlying health issues are preferred.
Who May Not Benefit?
- Advanced Joint Disease: Patients with widespread arthritis may not see significant improvement.
- Older Adults with Multiple Health Issues: Recovery may be more challenging for older patients with various health concerns.
- Unrealistic Expectations: It’s important to understand that while the surgery can improve function and relieve pain, it may not fully restore the joint.
A thorough evaluation by an orthopedic specialist at Ayushman Hospital can help determine if this surgery is right for you.
Preoperative Evaluation and Preparation
Before your surgery, you’ll undergo a thorough evaluation at Ayushman Hospital to ensure the best outcomes.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The process starts with a review of your medical history and a physical exam to assess joint function and overall health.
Diagnostic Imaging
Advanced imaging techniques (like MRI or X-rays) are used to:
- Determine the extent of cartilage damage.
- Identify underlying issues like bone spurs.
- Plan the precise location and size of the cartilage defect.
Consultation with Specialists
At Ayushman Hospital, you’ll consult with a team of specialists, including orthopedic surgeons, radiologists, and rehabilitation experts, to create a comprehensive care plan.
Preoperative Instructions
You’ll receive detailed instructions to prepare for surgery, including:
- Medications: Guidelines on which medications to stop or continue.
- Fasting: Information on fasting before the operation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Recommendations for diet and activity to promote optimal healing.
This thorough evaluation helps ensure you’re ready for a safe and effective surgery.
The Surgical Procedure in Detail
Let’s take a closer look at what happens during the surgery:
Step 1: Anesthesia
You’ll be given anesthesia to keep you comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
Step 2: Making the Incision
Once the anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon makes a small incision near the affected joint.
Step 3: Removal of Damaged Cartilage
The surgeon carefully removes the damaged cartilage, creating a clean area for the new cartilage.
Step 4: Harvesting Healthy Cartilage
- Autologous Procedure: A small sample of your own cartilage is taken from a non-critical area and processed in a lab.
- Allograft Procedure: If donor tissue is used, healthy cartilage is sourced from a donor.
Step 5: Implanting the New Cartilage
The surgeon carefully implants the healthy cartilage into the prepared site, ensuring it fits well with the surrounding area.
Step 6: Stabilization and Closure
Once the new cartilage is in place, the surgeon may use small devices or sutures to secure it. The incision is then closed.
Step 7: Final Assessment
Before concluding the surgery, the team checks that the implant is stable and that everything is properly aligned.
The entire process can take a few hours, depending on the complexity of your case.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Rehabilitation
After your surgery, recovery is a gradual process that involves several stages. Here’s what you can expect:
Immediate Postoperative Care
- Monitoring in Recovery: You’ll be closely monitored as you wake up from anesthesia. The medical staff will check your vital signs and manage any immediate discomfort.
- Pain Management: Pain medications will be given to keep you comfortable.
Hospital Stay
Your hospital stay can vary:
- Short Stay: Some patients can go home within 24 to 48 hours.
- Extended Stay: More complex cases may require a longer stay for observation.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation is essential for a successful recovery. Your physical therapy program will help:
- Restore Joint Function: Exercises will improve mobility, flexibility, and strength.
- Promote Healing: Gentle movements encourage blood flow to the joint.
- Prevent Complications: Structured rehabilitation helps avoid issues like stiffness and muscle weakness.
Long-Term Recovery
- Gradual Increase in Activity: You’ll gradually start increasing your activity levels, following your therapist’s guidelines.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Keeping up with your orthopedic surgeon for follow-up visits is important for tracking your progress.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Eating well and staying active will support your joint health long-term.
Successful recovery can take several months, but with commitment, many patients experience significant improvements in their joint function and a reduction in pain.
Success Rates and Expected Outcomes
Many patients see positive results from cartilage transplant surgery, leading to improved mobility and a better quality of life. However, individual outcomes can vary based on several factors:
Factors Affecting Success
- Extent of Damage: The size and location of the cartilage defect matter.
- Age and Health: Younger, healthier patients usually heal better.
- Adherence to Rehabilitation: Following your rehab program closely is critical.
- Surgical Expertise: The experience of the surgical team plays a big role in success.
What Patients Can Expect
- Pain Reduction: Most patients report less pain after recovery.
- Improved Mobility: Better joint function allows you to return to everyday activities.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: With reduced pain and improved movement, many feel a boost in their overall well-being.
Long-Term Outlook
While cartilage transplant surgery may not completely eliminate joint issues, it can significantly delay the need for more invasive procedures like joint replacement. Regular care and a healthy lifestyle are key to maintaining the benefits of your surgery.
Why Choose Ayushman Hospital, Dwarka, Delhi?
Ayushman Hospital is known for its expertise in advanced surgical procedures, including cartilage transplant surgery. Here are some reasons why patients choose this hospital:
Experienced Surgical Team
The hospital has a team of skilled orthopedic surgeons who specialize in joint surgeries. Their experience ensures you receive top-notch care.
State-of-the-Art Facilities
Ayushman Hospital is equipped with modern diagnostic and surgical tools, allowing for precise imaging and advanced surgical techniques.
Personalized Care
Every patient gets individualized attention. The team works closely with you to understand your unique needs, from evaluation to rehabilitation.
Comprehensive Postoperative Rehabilitation
The hospital has a dedicated rehabilitation unit where physical therapists design tailored recovery plans to help you regain full functionality.
Patient-Centric Approach
From your first consultation to follow-up visits, Ayushman Hospital prioritizes your comfort and understanding throughout the entire process.
Strategic Location
Located in Dwarka, Delhi, the hospital is easily accessible, making it a convenient option for patients in the area.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Hearing from others who have undergone this surgery can be inspiring. Many patients at Ayushman Hospital have shared their success stories:
- A New Lease on Life: One young athlete described how the surgery helped him return to sports after years of knee pain.
- Effective Pain Management: Many patients report a significant reduction in pain, allowing them to resume daily activities with ease.
- Improved Joint Function: Testimonials often highlight increased mobility and stability, enabling a more active lifestyle.
These experiences show that with the right care, cartilage transplant surgery can lead to a remarkable improvement in quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the main purpose of cartilage transplant surgery?
- The surgery aims to repair or replace damaged cartilage, reducing pain and improving mobility.
- How long is the recovery process?
- Recovery can vary, but expect several weeks for initial healing and up to six months for full rehabilitation.
- Is the surgery painful?
- While some pain is expected, modern pain management techniques help minimize discomfort.
- Who is an ideal candidate for this surgery?
- Ideal candidates are usually younger to middle-aged adults with localized cartilage damage and good overall health.
- How do I prepare for the surgery?
- Preparation includes a thorough medical evaluation, imaging, and consultations with the surgical team.
- Are there any risks involved?
- Potential risks include infection and incomplete cartilage integration, but careful planning helps minimize these.
- Can the surgery completely restore joint function?
- While the surgery can significantly reduce pain and improve function, it may not fully restore the joint.
The Journey to a Healthier Joint
Cartilage transplant surgery is more than just a procedure—it represents a journey toward a better, more active life. Deciding to undergo surgery is a big step, and it’s important to weigh the benefits and risks carefully.
A Step Towards Recovery
For many, the surgery is the first step in reclaiming independence. It offers the chance to return to activities that were once limited by pain. The journey begins with understanding cartilage damage and progresses through well-planned medical and rehabilitation steps.
A Collaborative Effort
Successful outcomes rely on teamwork between the patient, surgical team, and rehabilitation specialists. At Ayushman Hospital, this collaborative approach ensures you receive continuous care from the moment you decide to have surgery until you’ve fully recovered.
Embracing a New Lifestyle
After surgery, adopting a lifestyle that supports joint health is key. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine check-ups can help maintain your joint health and overall well-being.
Looking Forward
The field of cartilage transplant surgery is advancing rapidly. At Ayushman Hospital, ongoing improvements in surgical techniques and postoperative care are helping more patients enjoy better outcomes. There’s a bright future ahead for those seeking relief from joint pain.
Conclusion
Cartilage transplant surgery at Ayushman Hospital in Dwarka, Delhi, offers a modern solution for those struggling with joint pain. With advanced surgical techniques, personalized care, and comprehensive rehabilitation, the hospital is dedicated to restoring joint function and enhancing quality of life.
This guide has covered:
- The importance of cartilage for joint health.
- Common causes of cartilage damage.
- Different types of cartilage transplant procedures.
- The surgical process and recovery journey.
- Factors that influence success and expected outcomes.
- Why Ayushman Hospital is a trusted choice for this procedure.
If you’re considering cartilage transplant surgery, consulting with an orthopedic specialist is crucial. The path to better joint health is a collaborative one, and with the expertise at Ayushman Hospital, you can take confident steps toward a more active, pain-free life.
If you have further questions or want to schedule a consultation, don’t hesitate to reach out to Ayushman Hospital. Their dedicated team is ready to assist you every step of the way.
Thank you for reading this guide on cartilage transplant surgery. We hope it has provided valuable insights and answered your questions. Remember, your journey to better joint health is just a consultation away!
Book an Appointment Today!
🌐 Visit: www.ayushmanhhs.in
Would you like more information on costs, insurance, or doctor recommendations?