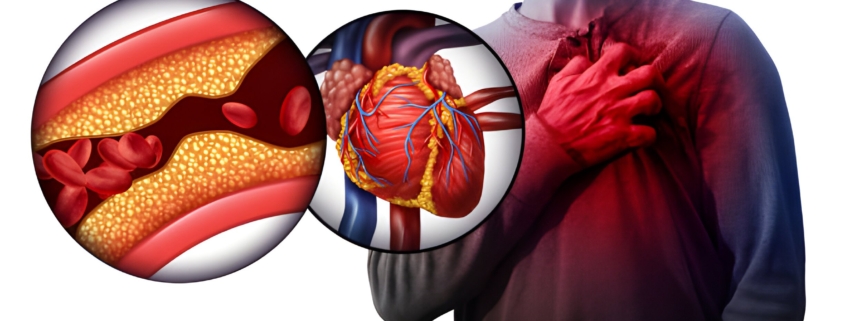
When it comes to heart health, time and expertise are key. If you have any symptoms, such as breathlessness, tiredness, or even discomfort in your chest, the decision to see a qualified cardiologist in Dwarka could be a lifesaver!! Dwarka is well equipped with advanced hospitals, cardiology specialty clinics, and experienced doctors – it is now a hub for trusted cardiac care. In this blog, we covered the importance of timing, quality specialists to consult, and why Ayushman Hospital is a top choice for your heart care.
Why consult a cardiologist in Dwarka?
Many people ignore the signs of heart problems until it is too late. Consulting with a cardiologist in Dwarka at an early stage can help diagnose and treat conditions like high blood pressure, arrhythmia (irregular or abnormal heartbeat), and blocked arteries. A cardiologist can also provide key diagnostic tools, including ECG and echocardiograms, lifestyle recommendations, and treatment advice to maintain your heart’s health.
Modern cardiac care in Dwarka includes an array of non-invasive tests, stress tests, and even high-end interventional options. It is difficult to talk about cardiovascular care without mentioning heart monitors, diagnostic and more chronic condition management with a cardiologist you trust; and having these options in Dwarka makes it seamless to obtain high-quality ongoing cardiac health care intervention.
Chest Pain Treatment in Dwarka – Don’t Overlook the Symptoms
Discomfort in the chest is one of the most common symptoms of heart problems. You might experience pressure, burning, and tightness in the chest area. Some people confuse their symptoms with acidity or muscular pain. Deathly errors are often made by ignoring or dismissing this type of discomfort. The hospitals that offer chest pain treatment in Dwarka are prepared to administer an emergency health checkup, including ECG, cardiac enzyme testing, and monitored intervention with a specialist that incorporates the risk of cardiac event into treatment.
Many heart complications, such as heart attack or cardiac arrest, can be prevented through quick action, leading to chest pain treatment in Dwarka. Women have been saved from serious heart conditions thanks to modern medicine, diagnostic capabilities, and through health interventions of trained professionals in the area of heart disease and heart complications.
Heart Disease Treatment in Dwarka – State-Of-The-Art Services
Many different types of heart disease can be simulated by coronary artery disease, heart attack, arrhythmias, or valve disease. Our healthcare infrastructure is tangibly growing and affording new advances for heart disease treatment in Dwarka. The range of treatment options includes medication or lifestyle change, cardiac rehabilitation, and interventional procedures such as cardiac catheterizations, angioplasty and stent placements.
Leading clinical hospitals and care facilities offer open heart disease treatment in Dwarka that includes examinations and testing appropriate for heart disease and recovery. Care model support continues to focus on comprehensive and inclusive approaches towards long-term heart health and prevention of acute cardiac events.
Ayushman Hospital In Dwarka – Reliable Cardiac Care
When it comes to reliable cardiac care, Ayushman Hospital Dwarka, New Delhi, stands out due to its clinical excellence, cutting-edge facilities, and compassionate staff. With a large team of experienced cardiologists and emergency response teams, Ayushman Hospital provides a one-stop place for everything related to heart disease. With 24×7 cardiac emergency care, ECG, and Echocardiography, and customized heart disease treatment in Dwarka, you’ll find everything in one location.
Ayushman Hospital has a department for chest pain treatment in Dwarka, allowing for rapid assessment and care for people in all age groups, making it one of the most trusted names in local heart care.
Conclusion
Your heart deserves expert care− and doesn’t need to be far away. Dwarka is fast becoming a reliable place to get the best cardiac care you can. Dwarka provides experience, modern facilities, and technology. If you’re looking for a cardiologist in Dwarka, fast chest pain treatment, or long-term heart disease treatment in Dwarka, quality hospitals like Ayushman Hospital will support your health journey.
FAQs – Cardiology and Heart Health in Dwarka
- When should I consult with a Dwarka cardiologist?
You should consult with a cardiologist if you are experiencing chest pain or persistent shortness of breath, if you have an irregular heartbeat, or if you have a family history of heart disease.
- What does chest pain treatment in Dwarka involve?
The hospital would likely start with an ECG, blood tests, and then a specialist would evaluate you to rule out or confirm cardiac causes of your pain.
- Who are the leading cardiologists at Ayushman Hospital?
The cardiology department is led by Dr. S.S. Murthy, Director & HOD, who has over 20 years of experience in clinical and invasive cardiology.
- Are pediatric cardiology services available?
Yes, Ayushman Hospital provides expert pediatric cardiology services for the treatment and management of congenital and acquired heart diseases in infants, children, and adolescents
- How can I book an appointment with a cardiologist at Ayushman Hospital?
Appointments can be booked by calling +91 9205481438 or visiting the hospital’s official website at www.ayushmanhhs.in.